Usage example: Euler characteristic curves¶
This notebook provides usage examples for the euchar.curve module.
Euler characteristic curves of 2D and 3D images with values sampled from uniform distributions.
Euler characteristic curves of finite point sets in \(\mathbb{R}^2\) and \(\mathbb{R}^3\), obtained using the Alpha filtrations on the finite point sets
import numpy as np
import euchar.utils
from euchar.curve import image_2D, image_3D, filtration
from euchar.filtrations import alpha_filtration_2D, alpha_filtration_3D, inverse_density_filtration
from euchar.display import piecewise_constant_curve
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.style.use("seaborn-whitegrid")
plt.rcParams.update({"font.size": 16})
from seaborn import distplot
Synthetic data¶
Images
np.random.seed(0)
m = 32
max_intensity = 256
img_2D = np.random.randint(0, max_intensity, size=(m, m))
img_3D = np.random.randint(0, max_intensity, size=(m, m, m))
Finite point sets
np.random.seed(0)
N = 100
points_2D = np.random.rand(N, 2)
points_3D = np.random.rand(N, 3)
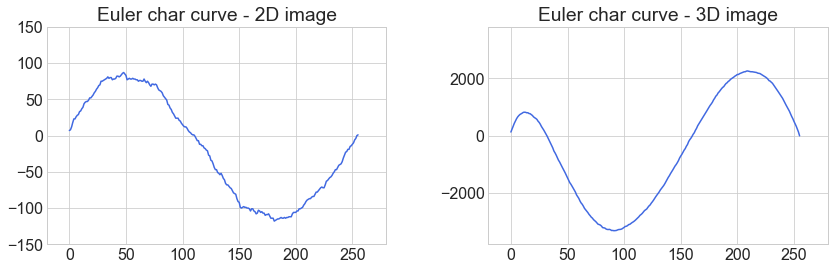
Euler characteristic curves of 2D and 3D image¶
For the following computation, the vector_2D_changes is
automatically computed by image_2D().
ecc_2D = image_2D(img_2D)
To avoid recomputing it every time, it can be passed as a parameter to
image_2D().
Precompute it with
vector_2D_changes = euchar.utils.vector_all_euler_changes_in_2D_images()
For the following computation, the vector of all possible Euler changes in the case of 3D images needs to be precomputed and saved to a file.
For example one could do this by running
vector_3D_changes = euchar.utils.vector_all_euler_changes_in_3D_images()
np.save("vector_3D_changes.npy", vector_3D_changes)
vector_3D_changes = np.load("vector_3D_changes.npy")
ecc_3D = image_3D(img_3D, vector_3D_changes)
We can then plot the Euler characteristic curves as piecewise constant curves.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14,4))
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.3)
domain = np.arange(256)
ax[0].plot(domain, ecc_2D, color="royalblue")
ax[0].set(title="Euler char curve - 2D image", xlim=[-20, 280], ylim=[-150, 150])
ax[1].plot(domain, ecc_3D, color="royalblue")
ax[1].set(title="Euler char curve - 3D image", xlim=[-20, 280], ylim=[-3_800, 3_800]);
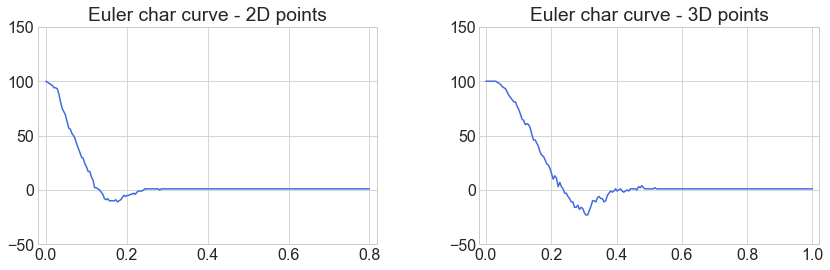
Euler characteristic curves of finite point sets¶
We obtain the Alpha filtrations in the form of arrays of indices of
points_2D and points_3D.
simplices_2D, alpha_2D = alpha_filtration_2D(points_2D)
simplices_3D, alpha_3D = alpha_filtration_3D(points_3D)
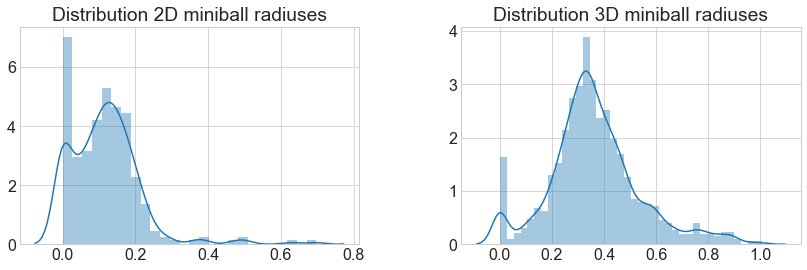
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14,4))
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.3)
_ = distplot(alpha_2D, ax=ax[0])
ax[0].set(title="Distribution 2D miniball radiuses")
_ = distplot(alpha_3D, ax=ax[1])
ax[1].set(title="Distribution 3D miniball radiuses");
We produce arrays bins_2D and bins_3D, used to discretize the
domains of the distributions of 2D and 3D Alpha parametrizations.
bins_2D = np.linspace(0.0, 0.8, num=200)
filt_2D = filtration(simplices_2D, alpha_2D, bins_2D)
bins_3D = np.linspace(0.0, 1, num=200)
filt_3D = filtration(simplices_3D, alpha_3D, bins_3D)
We plot the resulting Euler characteristic curves as piecewise constant curves.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14,4))
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.3)
ax[0].plot(bins_2D, filt_2D, color="royalblue")
ax[0].set(title="Euler char curve - 2D points", xlim=[-0.02, 0.82], ylim=[-50, 150])
ax[1].plot(bins_3D, filt_3D, color="royalblue")
ax[1].set(title="Euler char curve - 3D points", xlim=[-0.02, 1.02], ylim=[-50, 150]);